

We already know that viscosity refers to the friction of fluids. On the other hand, in the case of liquids, the viscosity shall decrease as the temperature increases. It is also essential to make a point of the fact that in the case of gasses, with the increase in the temperature, the viscosity will also increase. The viscosity of water is 0.001 Pa s, that of motor oil is 1, and that of air is 0.000019 Pa s. Furthermore, the more viscous a fluid is, the more resistance shall it offer to any object flowing or moving inside it. From the formula mentioned above, it is quite evident that if the velocity of the sphere increases, the viscosity will be more. We measure viscosity in Pascal seconds that is Pa s. We can, in turn, calculate v as the distance traveled by the sphere per unit time. Δρ = difference in the density of the fluid and the sphere tested Η = viscosity (represented by the symbol η or “eta”) If we drop a sphere into a fluid, we can calculate the viscosity using the formula specified below: The viscosity of a fluid is measured in terms of the ratio of its shearing stress (if the direction of external force on an object is parallel to the plane of an object, then the deformation will be along that plane, and the stress on the object will be shear stress) to its velocity gradient (the difference between the adjacent layers of a fluid). For instance - the viscosity of syrup is higher than that of water. So, we can say that the viscosity of a fluid refers to the measure of its resistance to gradual deformation at a given rate. In the example we discussed earlier concerning honey and water, we can say that honey is thicker than water due to which it is more viscous than water as well.

To be specific, viscosity defines a fluid's resistance to flow. The term 'Viscosity' in physics refers to the measure of the resistance of a fluid to gradual deformation by tensile stress (the force acting along the axis of force, which is responsible for the stretching or elongation of material) or shear stress (the external force on an object or surface area parallel to the plane or slope in which the object lies). Do you know the difference between both cases? The answer lies in the property of fluids, known as viscosity. In this particular scenario, the honey poured will take its own time running down the hair and face of that person. Now, let us consider another situation in which you pour 1000 ml of honey on a person's head. The effect of viscosity is important in a variety of disciplines, for example, in the study of fluids and gasses, as it governs their behavior.ĭo you know what will happen if you pour 1000 ml of water on a person's head? The water flows through the person's hair and then over the face. If the flow is a stream of uniform velocity, there is zero viscosity if, on the other hand, the velocity is turbulent and chaotic, there will be some viscosity.

If the fluid is caused to flow smoothly and regularly, there will be no viscosity. More simply, it is the resistance to a simple flow. In physics, Viscosity is defined as the measure of the resistance of a fluid to flow. The lower the interaction between the molecules of a liquid, the lower its viscosity, therefore there is less friction.The measure of a fluid's resistance to flow is known as viscosity. Liquids have a cohesion between their molecules that is weaker than a solid and stronger than a gas, which gives them the fluidity that characterizes them.
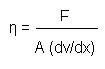
To understand both concepts, it is necessary to bear in mind that the viscosity of a fluid is determined by the level of cohesion of the molecules. Thus, it is important to know how liquids move in order to understand how mechanisms actuated by liquid fluids work. In hydraulics or fluid mechanics, dynamic viscosity and kinematic viscosity are necessary concepts to relate the forces that generate motion and velocity in a liquid. What are Dynamic and Kinematic Viscosity:ĭynamic viscosity and kinematics are values that determine the movement of a certain liquid or fluid under specific conditions. What are Dynamic and Kinematic Viscosity:.Video: Viscosity, dynamic viscosity & kinematic viscosity perfectly explained with physical feel Content


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
